Knee Arthritis Treatment Options

Osteoarthritis is a wear and tear disease. It typically occurs as we age and is the result of cartilage within the joint breaking down. This can cause pain and disability. Osteoarthritis (OA) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) are different. RA is an autoimmune disease. This is an outline of treatment options available to patients with OA. If you have RA these options are available for you to try as well. Patients with RA typically will need to see a rheumatologist to discuss specific medications not outlined in this guide.
1. Live with the problem the way that it is
Arthritis is not life threatening but is life limiting. Osteoarthritis symptoms can result in decreased activity levels and potential weight gain. These factors can result in higher risk for cardiovascular events.
2. Lifestyle modification including weight loss and activity change
This includes healthy eating, exercise, physical therapy/aqua therapy.
Adhering to a low carbohydrate diet and refraining from highly processed foods is the key to a healthier lifestyle. Ask us about referring you to a nutritionist. Some insurance companies cover this service.
Low impact exercise such as biking, walking and swimming can improve pain and function for patients with osteoarthritis.
Did you know that even 5 lbs. of additional weight adds around 20 lbs. of pressure to an arthritic knee?
Using a cane or walker may help offset the pain that osteoarthritis causes while weight bearing.

3. Oral or topical medication
This includes acetaminophen (Tylenol), anti-inflammatories (Ibuprofen, Advil, Aleve, Celebrex, Meloxicam), CBD and supplements (Glucosamine, Chondroitin).
Tylenol
Most patients can safely take Tylenol for their arthritis pain.
NSAIDS (anti-inflammatories)
Patients with history of stomach ulcers, significant cardiac history, kidney disease, history of gastric bypass or patients on a blood thinner should not use oral NSAIDs. Topical medications and patches (Voltaren Gel, Mountain Ice, Salonpas) can also be helpful with lower side effects reported. Ice can also act as an anti-inflammatory.
CBD
There are studies now indicating that CBD can be helpful in relieving arthritis pain. CBD, unlike THC, does not cause mind altering effects.
Glucosamine/Chondroitin
There are several studies showing modest pain relief reported from using supplements. Supplements do not restore or slow degeneration of the cartilage.
Narcotics
Narcotics are not effective in reducing pain and improving function in osteoarthritis.
4. Intra-articular injections such as Cortisone, Toradol and Viscosupplementation

Cortisone is a steroid meant to decrease inflammation within the joint and improve pain. This medication may affect blood sugar. Some insurance companies will authorize a steroid injection for our diabetic patients that will not increase blood sugar. Please ask us about it.
- Cortisone injections may provide pain relief for up to 90 days. This outcome depends on how severe your arthritis is. Patients with severe, bone on bone arthritis may only benefit a few weeks from this type of injection. You can have an injection once every 3 months if needed. There is some concern that these injections can cause further cartilage damage in the joint. However, these injections are still widely used and may help certain patients delay joint replacement. Symptoms may improve after 3 days of the injection. Some patients report delayed onset of relief.
- Unfortunately, 2% of patients who receive a cortisone injection can experience a flare up of pain related to the injection. This typically subsides within 72 hours and the injection can still help with the arthritis pain you were previously experiencing. Patients receiving cortisone injections may also experience facial flushing for up to 48 hours. Women more commonly experience this symptom. This is not an allergic reaction or medical emergency but can be uncomfortable.
Viscosupplementation also known Hyaluronic acid (HA) is often referred to as gel injections. These injections are lubricating agents. HA is not currently recommended by The American Academy of Orthopedics. Studies do not show significant improvement in function or long-term pain relief with HA especially in patients with severe OA. These injections are more likely to help in a patient with mild to moderate OA. Despite this, we have had some success with HA injections.
- The injections may not be covered by certain insurance companies. Many companies require preauthorization. The injections are usually a series of 3 (once a week for 3 weeks) and you can receive them every 6 months. Some patients report pain, stiffness and swelling after these injections. It may take up to 4 weeks after the last injection before symptoms improve.
Toradol is an anti-inflammatory which can provide up to 3 months of pain relief, like Cortisone. However, this injection will not increase blood sugar. Pain flare is not typically associated with Toradol. Patients with severe arthritis may not experience long term, significant relief. This injection is used less frequently than cortisone or HA.
*All injections have a very small risk of infection, well under 1%.
5. Biologic treatments such as PRP or stem cell injection.
Current research is showing BETTER pain relief and improved function with PRP over cortisone and HA injections. Unfortunately, these treatment options are not covered by insurance and can be costly. Currently the Academy of Orthopedics encourages only those patients with mild to moderate arthritis to consider biologic treatments. This may be an option for a young patient needing to delay joint replacement. We currently only offer PRP. Studies have shown patients reporting pain relief for up to one year after a PRP injection. If you are interested in this treatment option, we have additional information for you.
6. Cryotherapy
We offer a treatment called Iovera.
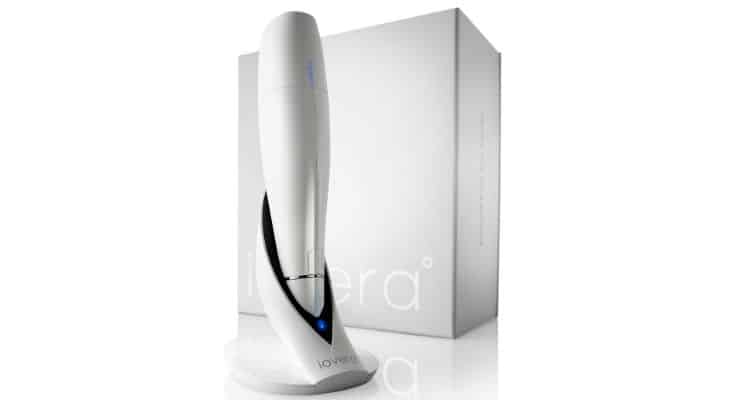

This is a nerve freezing procedure. There are studies showing improved pain and function after Iovera treatment. This treatment is more likely to help someone with mild to moderate OA. Again, some insurance companies have resisted covering this treatment. Many people undergo this procedure prior to knee replacement to control postoperative pain. Keep in mind Iovera will not help patients with lateral (outside) compartment arthritis. If you have questions about this treatment option, we have additional information for you.
There is another procedure called Coolief that targets deeper nerves that ultimately may help with pain relief better than Iovera. The Coolief website has a list of providers offering this treatment. Albany is the closest area to us offering Coolief.
Our local pain management doctors also offer nerve blocks for knee pain which may provide short term pain relief. If this is something you are interested in, you will need a referral.
7. Acupuncture
This is an alternative treatment to the most common ways to treat pain from osteoarthritis. Again, insurance companies tend not to cover this type of procedure.
There are studies showing knee pain improvement after acupuncture.
8. Knee replacement either a total knee or partial knee replacement.
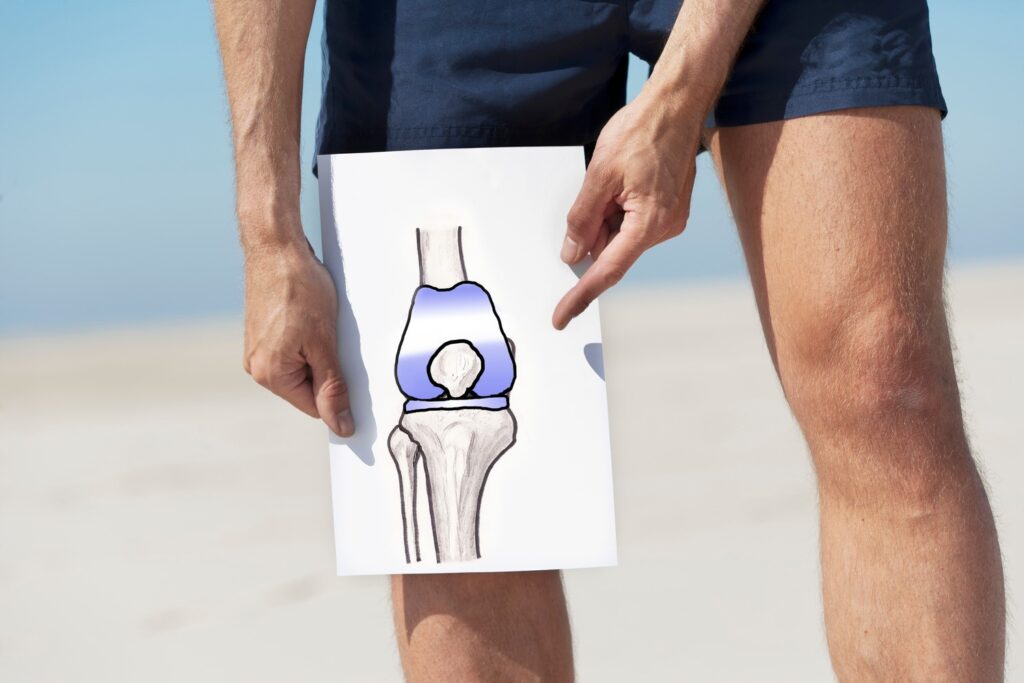
Talk to your provider to see which surgery you are a candidate for. Knee replacement requires commitment from both you and your family or friends. You should have pain in your knee every day that limits your abilities to perform routine activity before considering this procedure. Recovery takes at least 8 weeks of restricting walking, performing hourly exercise, icing and elevating. We have a lot of information for you about knee replacement. Let us know if you are considering surgery.
On The Fence?
Not sure if your knee is bad enough for surgery? You can take a quiz that may help you decide if you’re ready for knee replacement.
Open your phone’s camera and scan the QR code below to take you to the quiz website.

Once you finish the questionnaire you can ask one of our providers to help you review the results.
The lower you score on this quiz indicates worse pain and disability. The average score for a patient 2 years AFTER total knee replacement is 85. (100 is a perfect knee-18 year old’s knee score) Your score should be under 60 (even better if under 50) to be reasonably happy with a total knee.
American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. AAOS. (2024)
American Association of Hip and Knee Surgeons. AAHKS. (2024)
Hip Arthritis Treatment Options

Osteoarthritis is a wear and tear disease. It typically occurs as we age and is the result of cartilage within the joint breaking down. This can cause pain and disability. Osteoarthritis (OA) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) are different. RA is an autoimmune disease. This is an outline of treatment options available to patients with OA. If you have RA these options are available for you to try as well. Patients with RA typically will need to see a rheumatologist to discuss specific medications not outlined in this guide.
1. Live with the problem the way that it is
Arthritis is not life threatening but is life limiting. Osteoarthritis symptoms can result in decreased activity levels and potential weight gain. These factors can result in higher risk for cardiovascular events.
2. Lifestyle modification including weight loss and activity change
This includes healthy eating, exercise, physical therapy/aqua therapy.
Adhering to a low carbohydrate diet and refraining from highly processed foods is the key to a healthier lifestyle. Ask us about referring you to a nutritionist. Some insurance companies cover this service.
Low impact exercise such as biking, walking and swimming can improve pain and function for patients with osteoarthritis.
Did you know that even 10 lbs. of additional weight adds over 25 lbs. of pressure to an arthritic hip?
Using a cane or walker may help offset the pain that osteoarthritis causes while weight bearing.

3. Oral or topical medication
This includes acetaminophen (Tylenol), anti-inflammatories (Ibuprofen, Advil, Aleve, Celebrex, Meloxicam), CBD and supplements (Glucosamine, Chondroitin).
Tylenol
Most patients can safely take Tylenol for their arthritis pain.
NSAIDS (anti-inflammatories)
Patients with history of stomach ulcers, significant cardiac history, kidney disease, history of gastric bypass or patients on a blood thinner should not use oral NSAIDs. Topical medications and patches (Voltaren Gel, Mountain Ice, Salonpas) can also be helpful with lower side effects reported. Ice can also act as an anti-inflammatory.
CBD
There are studies now indicating that CBD can be helpful in relieving arthritis pain. CBD, unlike THC, does not cause mind altering effects.
Glucosamine/Chondroitin
There are several studies showing modest pain relief reported from using supplements. Supplements do not restore or slow degeneration of the cartilage.
Narcotics
Narcotics are not effective in reducing pain and improving function in osteoarthritis.
4. Intra-articular injection
This is not a treatment option we frequently recommend. Unfortunately, injections into the hip joint do not typically provide worthwhile, long term pain relief. There is also a small infection risk with injecting the hip socket.
Patients that are too young for surgery, elderly or have multiple medical issues may consider this option. Our local pain management providers do offer these injections and if we think you are a candidate for injection, we can refer you.
HA injections are not approved for hip arthritis. We are also not offering PRP injections for hip arthritis.
5. Acupuncture
This is an alternative treatment to the most common ways to treat pain from osteoarthritis. Again, insurance companies tend not to cover this type of procedure.
There are studies showing knee pain improvement after acupuncture.
6. Hip Replacement
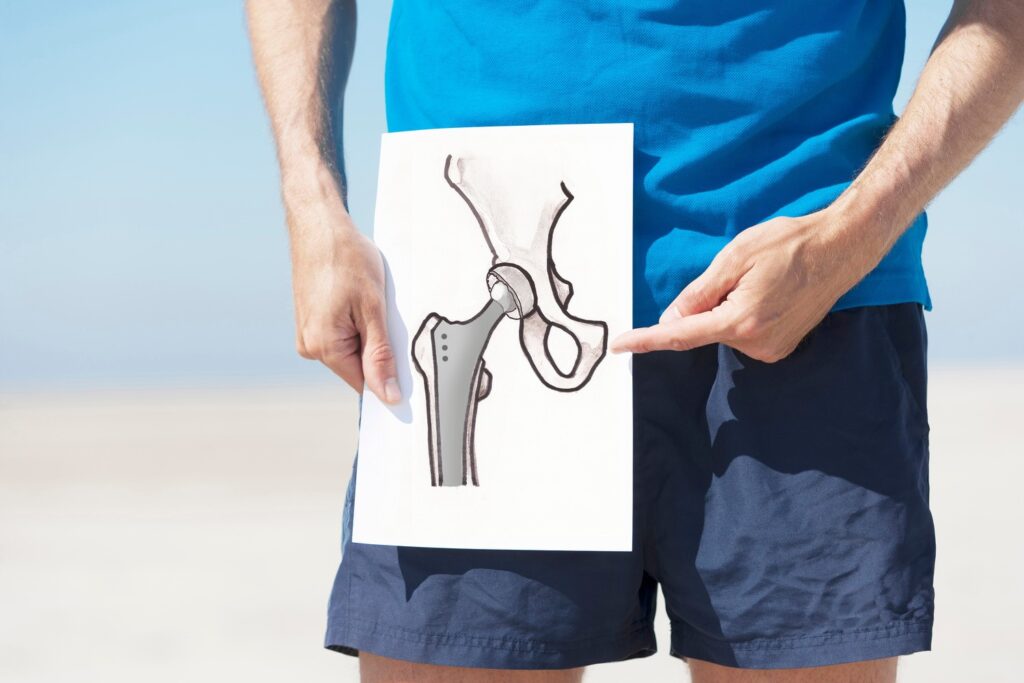
Hip replacement requires commitment from both you and your family or friends. You should have pain in your hip every day that limits your abilities to perform routine activity before considering this procedure. Recovery takes at least 8 weeks of restricting walking, performing hourly exercise, icing and elevating. We have a lot of information for you about hip replacement. Let us know if you are considering surgery.
On The Fence?
Not sure if your hip is bad enough for surgery? You can take a quiz that may help you decide if you are ready for hip replacement.
Open your phone’s camera and scan the qr code below to take you to the quiz website.

Once you finish the questionnaire you can ask one of our providers to help you review the results.
The lower you score on this quiz indicates worse pain and disability. The average score for a patient 2 years AFTER replacement is 85. (100 is a perfect knee-18 year old’s hip score) Your score should be under 60 (even better if under 50) to be reasonably happy with a total hip.
American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. AAOS. (2024)
American Association of Hip and Knee Surgeons. AAHKS. (2024)
